Sometimes men are faced with such an unpleasant disease as bacterial prostatitis. In order to start treatment on time, it is important to know by what signs the disease can be determined and what diagnostics and treatment will be required.
Bacterial prostatitis is an infectious disease of the prostate. Symptoms of the disease include pain in the perineum, increased body temperature, intoxication of the body, and other signs. Such a condition may require emergency hospitalization, as it can pose a threat to the health and life of the patient.
Forms of bacterial prostatitis
Depending on the course and symptoms manifested, bacterial prostatitis is divided into two forms - acute and chronic.
Sharp
The acute form manifests itself unexpectedly and is accompanied by various unpleasant symptoms. The acute form of bacterial prostatitis requires immediate medical attention. This pathological process is provoked by Escherichia coli, staphylococci, enterobacteria.
Acute prostatitis is easily diagnosed with the help of laboratory tests. Severe symptoms and a clinical picture allow an accurate diagnosis. Treat this form of prostatitis in a complex way using drugs and physiotherapy.
Chronic
Chronic bacterial prostatitis has a pathogen that can be determined using tests and laboratory studies. The main pathogens are gonococci, chlamydia, ureaplasma, mycoplasmas. The inflammatory process can also be caused by tuberculosis bacteria or fungi of the genus Candida, if the man is infected with HIV.
Types of bacterial prostatitis
Bacterial prostatitis is classified by type of pathogen:
- tuberculous (Koch's bacillus);
- gonorrheic (gonococci);
- fungal (various types of fungi);
- chlamydia (chlamydia);
- viral (agents responsible for herpes, human papillomavirus, influenza);
- mixed (several different infections).
It is possible to determine what exactly was the causative agent only under laboratory conditions, since the symptoms are the same for everyone.
Causes and risk factors
The bacteria enter the prostate, causing acute or chronic prostatitis. Sexually transmitted diseases can also cause this disease. In some cases, the cause cannot be determined.
Responsible officersbacterial prostatitis are considered:
- colibacillus;
- klebsiella;
- Proteus;
- faecal enterococcus;
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Possiblemicrobiological reasonsprostatitis are:
- staphylococci (saprophytic, golden, epidermal);
- genital mycoplasma;
- Chlamydia trachomatis;
- ureaplasma;
- Trichomonas.
TOrisk factorsinfection of the prostate with the further development of the inflammatory process in the form of one or another form of bacterial prostatitis are:
- intraprostatic reflux (reflux of urine into the prostate ducts during urination);
- pelvic injury;
- unprotected anal sex;
- urinary tract infections;
- have an indwelling urethral catheter or intermittent bladder catheterization;
- transurethral diagnostic and therapeutic interventions;
- HIV AIDS;
- previous prostate biopsy.
Symptoms of bacterial prostatitis
Usually with bacterial prostatitis the symptoms are so pronounced that it is difficult not to pay attention to them. Signs of illness include:
- high body temperature (in the anus is usually higher than in the armpits);
- fever and chills;
- difficult and painful urination, especially at night;
- possible development of constipation due to prostate enlargement;
- pain in the lower body (lower back, perineum, lower abdomen);
- general intoxication of the body;
- discharge from the urethra and blood in the semen.
Stages of bacterial prostatitis
The clinical picture of bacterial prostatitis manifests itself depending on the stage of the disease and the degree of involvement of prostate tissue in the inflammatory process. To share:
- Primary or catarrhal prostatitis.It is characterized by inflammation of the walls of the prostate. It is quite possible to cure it with antibiotics in 10 days.
- Secondary or follicular.It is characterized by the formation of abscesses in the glandular tissue. It is accompanied by a high fever. This form is also effectively treated with antibacterial drugs.
- Tertiary or parenchymal.The pathological process at this stage extends to the entire organ - the prostate increases in size, swells and changes shape. If you do not take timely treatment, the tertiary stage may progress to chronic prostatitis.
Possible complications and consequences for men
The consequences and complications of bacterial prostatitis include:
- vesiculitis (inflammation of the seminal vesicles) - manifested by groin pain, premature ejaculation, painful erection;
- colliculitis (inflammation of the seminal tubercle) - is distinguished by various symptoms - burning and tickling of the posterior urethra, painful sensations during orgasm, blood in semen;
- violation of potency;
- sclerosis of the prostate;
- infertility;
- prostate cyst;
- abscess of the prostate;
- stones in the prostate.
Chronic pelvic pain syndrome is one of the most serious consequences of chronic prostatitis.
Asymptomatic inflammation is the mildest form in terms of the absence of complaints. This type of prostatitis is diagnosed with the development of complications of reproductive function.
Is bacterial prostatitis dangerous for women?
Prostatitis in women does not occur, but its serious consequences are common. If a man has bacterial prostatitis, it is simply irresponsible to say that a woman is not in danger: chlamydia, ureaplasma, Trichomonas, mycoplasma, gonococcus, gardnerella and other infections received by her from a partner have aserious danger to a woman and lead to the development of various gynecological diseases.
Which doctor treats?
Urologistis considered the main specialist who deals with the diagnosis and treatment of pathological conditions of the genitourinary system.
Andrologist.Despite the fact that andrology belongs to a fairly young branch of medicine, specialists in this field are gradually taking their place in the treatment of diseases of the male genitourinary system. The advantage of this doctor is his narrow focus. Unlike a urologist who treats diseases of the male and female genitourinary systems, the andrologist specializes exclusively in male problems.
Diagnosis of bacterial prostatitis
If bacterial prostatitis is suspected, a number of tests are done, including:
- scrapings and swabs for infection;
- cultures for flora and sensitivity to antibiotics;
- a general blood test helps to detect the inflammatory process, when there is an increase in the number of leukocytes, an increase in ESR;
- spermogram, which examines a decrease in the number of sperm, a violation of their mobility;
- three-glass urine sample (studies inflammatory changes in urine);
- general urinalysis;
- analysis of the secretion of the prostate;
- flowmetry - observation of the daily amount of urine.
The doctor will be able to assess how enlarged the prostate is with a digital rectal exam. To clarify the diagnosis, the doctor may refer you to a transrectal ultrasound.
Treatment of bacterial prostatitis
As a treatment for bacterial prostatitis, drugs, physiotherapy, folk remedies are prescribed, and in severe cases, surgery.
Medical treatment
Medical treatment of prostatitis is carried out with the help of various groups of drugs. These may be antibiotics to neutralize the pathogen. However, they do not always help, because the prostate is characterized by poor absorption of antibiotics from the group of protected penicillins, fluoroquinolones.
Treatment usually lasts 10-14 days and should be completed without fail, because if bacterial prostatitis is left untreated, it will come back. Vitamins and drugs are also prescribed to strengthen the immune system.

Surgical intervention
The doctor offers surgery for prostatitis if no results have been obtained in treating a patient with drugs, physiotherapy, or alternative methods of treatment.
The surgical intervention includes the following procedures:
- Transurethral resection of the prostate.The internal part of the organ is removed. Surgery is the most commonly used and best endoscopic treatment for benign prostatic hyperplasia.
To perform this procedure, the patient undergoes a number of tests, including blood and urine tests. The operation is performed under spinal anesthesia, but general anesthesia can also be used. There are no scars after the operation. Among the minuses there is painful urination in the first days after the procedure. - Laser surgery.The laser destroys diseased tissue. At the same time, the size of the prostate decreases and the vessels are "sealed" and do not bleed. The operation is performed without incisions and the postoperative period is only three days. Before the procedure, blood and urine tests are done, as well as an ultrasound of the urinary tract and, as prescribed by the doctor, a biopsy of the prostate is taken.
This method is not effective if the prostate is large. - Open prostatectomy.The operation is performed in cases when the prostate is greatly enlarged, in the presence of complications and in case of damage to the bladder.
The surgeon makes an incision either in the lower abdomen or between the scrotum and the anus. Either part of the prostate is removed or it is completely removed.
Before the operation, an ultrasound, MRI and cytoscopy are performed, as well as blood and urine tests and a prostate-specific antigen test.
One of the advantages of the operation is its effectiveness in treating the prostate and related problems. And among the minuses - a long period of postoperative recovery (more than a month), as well as problems with erectile function. - Transurethral incision of the prostate.The doctor does not remove prostate tissue, but only makes an incision to relieve pressure on the urethra, making it easier to urinate. Before the operation, blood and urine tests are done, as well as an ultrasound of the urinary tract.
Benefits of the procedure - symptoms of prostatitis are relieved without the risk of retrograde ejaculation, long-term recovery is not required. Among the shortcomings - prostatitis still needs to be treated. - Prostate abscess drainage.The doctor opens the abscess through the perineum or rectum, dissecting the skin and subcutaneous tissue and introducing drainage into the cavity with pus for removal.
Before the operation, a consultation with a proctologist is carried out, blood and urine tests are carried out.
The advantages of the operation include the absence of risk of loss of sexual functions. The downsides are that the abscess may not be completely removed and bacteria can spread throughout the body.
Surgery for prostatitis in men is usually a last resort for chronic bacterial prostatitis associated with complications of any form.
Physiotherapy
In the complex treatment of patients with a diagnosis of prostatitis, the physical methods of influence are of great importance. As a result of physiotherapy procedures, the following are improved:
- blood flow;
- lymphatic drainage, which contributes to the removal of decomposition products of microorganisms;
- blood and lymphatic circulation, due to which inflammatory infiltrates are resolved;
- discharge of blood and lymph, which helps reduce congestion in the pelvis;
- metabolism;
- the activity of cell membranes, which promotes the penetration of active drugs into the cell.
Physiotherapy for bacterial prostatitis includes the following methods:
- Electrophoresis.Impact on the body with ions, which helps relieve inflammation and eliminate pain.
- Laser physiotherapy.The laser helps relieve perineal pain and improves blood flow to the pelvic organs. It kills bacteria and removes waste from harmful organisms.
- Magnetotherapy.When performing this procedure, the permeability of the tissues improves, and the effectiveness of drug therapy increases significantly. In addition, with the help of magnetotherapy, hemodynamics and congestion are stopped.
Exercise for bacterial prostatitis
Exercise for chronic prostatitis causes the muscles of the pelvic region to contract, which ensures a difference in intra-abdominal pressure. This promotes blood flow to the prostate. Exercise tones the nervous system, makes the adrenal glands work, and removes the residual effects of inflammatory prostate disease.
You can do the following exercises at home:
- The man sits on a rubber ball and rolls from side to side, jumping slightly. It helps strengthen the pelvic floor muscles and the obliques.
- Kegel exercises. For 5-10 seconds, tense the buttocks as much as possible, then relax the muscles. This exercise is performed 20-50 times.
- Lying on your back, bend your knees and put your heels on the floor. Slowly raise your pelvis while keeping your upper back flat on the floor. When the pelvis is at the top, you need to freeze for 15 seconds and then return to its original position. The number of repetitions is 10 to 15 times.
Perform a massage
To achieve the result, exercises are carried out every day and are also supplemented by massage of the prostate, which can be performed both independently and with the help of special massagers.
Self-massage of the prostate is carried out as follows:
- Drink a liter of water one hour before the procedure to fill the bladder.
- Cleanse the intestines with an enema based on a solution of potassium permanganate or chamomile infusion. The crotch should be rinsed.
- Hands should be washed thoroughly and nails cut short.
- You must put a glove or a condom on the finger that will be used for the massage.
- The rubber surface of the protective layer is lubricated with petroleum jelly, grease or baby cream.
- Lie down in a comfortable position and insert your finger into the anus to a depth of 5 cm.
- On the front wall you can feel the prostate and start to stimulate it with light strokes from the sides to the center.
- On hard areas, the pressure is gradually increased, and on soft areas, it is reduced.
- At the final stage, stroking movements are made downward along the central groove.
- Gently remove your finger from the anus.
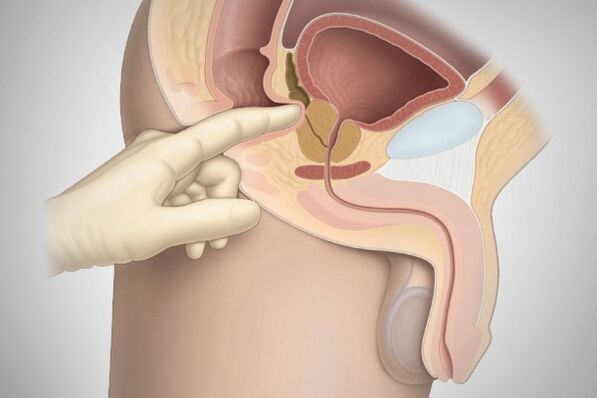
During the massage, 3-5 drops of liquid (prostate juice) should be released. Immediately after the massage, you need to go to the toilet and empty the bladder.
Diet therapy
With prostatitis, it is necessary to reduce the consumption of alcohol and cigarettes as much as possible. In addition, doctors recommend excluding from the diet:
- fatty foods, especially meat, because fat is a source of "bad" cholesterol, which disrupts blood circulation and negatively affects the prostate;
- energy and synthetic drinks;
- spices;
- spicy and smoky.
It is recommended to eat boiled and steamed food, a lot of vegetables and herbs.
Folk remedies
Pumpkin seeds.Pumpkin seeds are an old remedy for prostatitis. They contain a lot of zinc, which the male body needs. You should eat 30 seeds a day before meals.
Hazelnut branches.Boil several sprigs of hazelnut with leaves in water for 20 minutes, leave to infuse until the broth acquires a red-brown color. For a cure, a weekly course is sufficient.
Aspen bark.Aspen bark should be harvested at the very beginning of the sap flow period, before the buds bloom. It is approximately the second half of April. Dry the bark in the oven, take 100 g, grind and put in a half-liter jar. Pour 200 g of vodka so that the rind is completely covered. Close the jar and place it in a dark place for 2 weeks. Filter after 2 weeks. Take 1 teaspoon in three three week courses with a 10 day break.
Prognosis of bacterial prostatitis
The prognosis for bacterial prostatitis depends on the stage and type of the disease. The duration of the disease also affects the prognosis - the longer the inflammation is maintained, the longer it takes to treat complications of prostatitis.
In acute prostatitis, the prognosis is favorable. Chronic bacterial prostatitis is often a recurrent form, even when conservative therapy is prescribed. With long-term treatment of the chronic form, changes in potency may occur.
Preventative measures
Prevention of bacterial prostatitis can be divided into primary and secondary.
Primary prevention of prostatitis:
- healthy lifestyle;
- Good nutrition;
- play sports.
Preventive measures at home are important - performing exercises that activate blood circulation in problem organs and improve muscle tone.
In addition, men should study Kegel exercises. They were developed for postpartum recovery in women, but they are used to train a man's anal muscles and rectum.
Gymnastic exercises are useful: bicycle, birch, bridge, candles. They train the pelvic muscles. It is recommended to perform leg movements, apnea exercises and to take a contrast shower.
Secondary prevention of prostatitis:
- medical treatment;
- regular examination by a urologist, regardless of the manifestations;
- in the year after treatment, undergo quarterly examinations, later - once every six months.
For secondary prevention, rectal suppositories are used. They work through the rectum. Usually, these drugs have few contraindications. Also, to prevent the recurrence of bacterial prostatitis, biologically active drugs are prescribed.
The earlier prostatitis is detected, the easier it is to cure. Therefore, do not neglect regular visits to the doctor. After the diagnosis, the doctor will select the appropriate drugs and prescribe a therapeutic course. If the disease progresses, taking medication on time will quickly relieve symptoms and help you stay active and functional.































