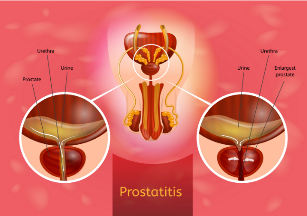
Prostatitis – this is a disease of the prostate (prostate cancer), emerging in the result of inflammatory changes in it. According to statistics, the prevalence of the disease reaches 35-50%, and revealed in men aged 20-40 years.
Types of
Issue 4 forms of prostatitis:
- acute (bacterial);
- chronic bacterial;
- chronic non-bacterial;
- asymptomatic chronic.
Acute prostatitis occurs very rarely, because the rapid flow of the inflammatory process and for an immediate transition to the chronic phase (faux improvements).
Chronic non-bacterial prostatitis, otherwise, his so-called syndrome of chronic pelvic pain may have an inflammatory (with the presence in the urine and ejaculate the increased content of leukocytes) and do not have an inflammatory character.
Reasons
The cause of acute and chronic bacterial prostatitis are pathogenic microorganisms (viruses, bacteria, fungi). The most common source of inflammation are:
- escherichia coli;
- streptococci;
- staphylococci;
- Proteus;
- Klebsiella;
- Pseudomonas wand;
- activators of diseases, sexually transmitted infections (chlamydia, mycoplasma, gonorrhea, Trichomonas, cytomegalovirus, and others).
A large part of the micro-organisms located in the gut, on the skin of the skin, but to get into the tissue of the prostate gland, which cause an inflammatory process. As usual, the cause of the disease is not one causative agent, but the association of more types of microbes.
The development of chronic prostatitis can trigger the following factors:
- related diseases of the urinary system (cystitis, pyelonephritis);
- a sedentary lifestyle ("sedentary" work);
- a tendency to constipation;
- the weakening of the defensive forces of the organism;
- injury;
- the hormonal imbalance;
- alcohol abuse and smoking;
- a promiscuous sexual connection;
- irregular sexual life (prolonged abstinence);
- interrupted sexual intercourse;
- irregular emptying of the bladder;
- unsatisfied sexual desire;
- chronic stress;
- hypothermia;
- the availability of carious teeth and other sources of chronic infection (for example, chronic inflammation of the tonsils).
Symptoms of prostatitis
Acute prostatitis - a very insidious disease. "Catch" is that hard enough, because, firstly, this process is very fast becoming chronic, and secondly, most patients prefer to "sit" manifestations of acute prostatitis of the house. To doctors, patients with inflammation of the prostate often turn already in advanced cases with erectile dysfunction and other consequences.
The acute form of the disease occurs in the background:
- an elevated temperature;
- chills;
- other symptoms of intoxication (weakness, lethargy, loss of appetite, etc.).
Inflammation of the prostate gland is accompanied by pain in the groin, in the groin and on the scrotum.
Typical is also painful and frequent urination. Sometimes in the urine may notice a whitish purulent discharge.
In addition, the pain may pay attention to the lack of nocturnal and morning erections, poor erections during intimacy and drastic shortening of sexual intercourse.
Symptoms of chronic bacterial prostatitis may be missing or appear in the period of exacerbation. For this stage are typical pain in the groin and lower abdomen, often radiating in the sacrum, lower back and scrotum.
They appear typical symptoms of disorders of urination: weak urine stream and frequent urination, even if the urine sticks out a little bit.
In the future, if left untreated chronic prostatitis reaches a peak: there are disorders of sexual function. For example:
- the lack of an erection or the lack of it;
- painful erection, because of which the patient avoids sexual acts;
- effacement orgasm;
- short sexual intercourse;
- soreness ejaculation.
Bad and the overall condition of the men: it is quickly tired, constantly irritable, sleeps poorly.
Chronic abacterial prostatitis is 95% of all prostatitis, get sick of them, mostly men around 30 years. It is characterized by continuous or periodic pain in the area of small pelvis, prostate, scrotum, taking in the laboratory analyses of missing signs of inflammation. The causes of the disease are not accurately determined.
Diagnosis
When the diagnosis of acute and chronic prostatitis in addition to collecting complaints, anamnesis and examination of the patient are used the following methods:
- the general analysis of blood and urine;
- microscopic examination of prostate secretion and sowing on nutritious environment for the identification of the pathogen (the secret of after a thumb massage of the prostate through the rectum);
- cytological examination of the urine;
- ULTRASOUND of the prostate and the pelvic organs;
- computed tomography and nuclear magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- a swab from the urethra on the microflora.
Differential diagnosis is focused on the definition of the prostatitis, prostate adenoma, prostate cancer, symptoms of stones in the prostate gland.
A complete list of diagnostic procedures and drugs for the treatment of prostatitis in a Federal standard of care from 2012.
Treatment of prostatitis
The same symptoms can be symptoms of various diseases, and the disease can progress not according to the textbook. Do not try to treat yourself, consult with your doctor.
Treatment of prostatitis leads the surgeon-urologist.
The aim of causal treatment aimed at removing the causes of prostatitis, is the elimination of the pathogen. Depending on the identified causes are assigned to antibiotics, antiviral or antifungal drugs. The length of therapy in the acute prostatitis is 7-10 days, during chronic process - 4-8 weeks.
For the treatment of a bacterial infection are used:
- antibiotics fluorinated quinoline series (ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, moxifloxacin);
- macrolides (erythromycin, clarithromycin);
- doxycycline;
- antibacterial medications.
Antifungal called oral and rectal candles.
In addition to using another therapy:
- anti allergic;
- anti-inflammatory;
- relief from the pain.
Are also:
- physiotherapy;
- physiotherapy;
- massage of the prostate.
The whole course of treatment lasts 3-4 months.
Complications
Not cure the prostatitis is dangerous to the following complications:
- the obstacles of the urinary bladder with subsequent acute retention of urine;
- infertility;
- relapses of inflammation of the urinary bladder;
- abscess of the prostate;
- depression;
- impotence;
- adenoma of the prostate;
- calculous prostatitis (stone similar with debilitating pain);
Weather
The prognosis in acute prostatitis favorable, early treatment leads to a full recovery. The frequency of exacerbations during long-term exposure of prostatitis reaches 50% and higher, but when appropriate to support the treatment it is possible to achieve an open forgiveness.
Prevention
For the prevention of disease, it is necessary to observe the following conditions:
- regular sexual life with the constant partner;
- refusal of bad habits;
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle (sport, walks in the fresh air);
- compliance with the diets;
- regular visits to the urologist.































